Data Wranglers can be viewed as a specialised type of data scientist, primarily working in the space between data generators and data analysts. There are many activities that a data scientist might undertake, for example, data collection, wrangling, analysis, modelling, visualisation and communication. How these activities map onto different job titles is domain specific and will vary on a project and organisational level.
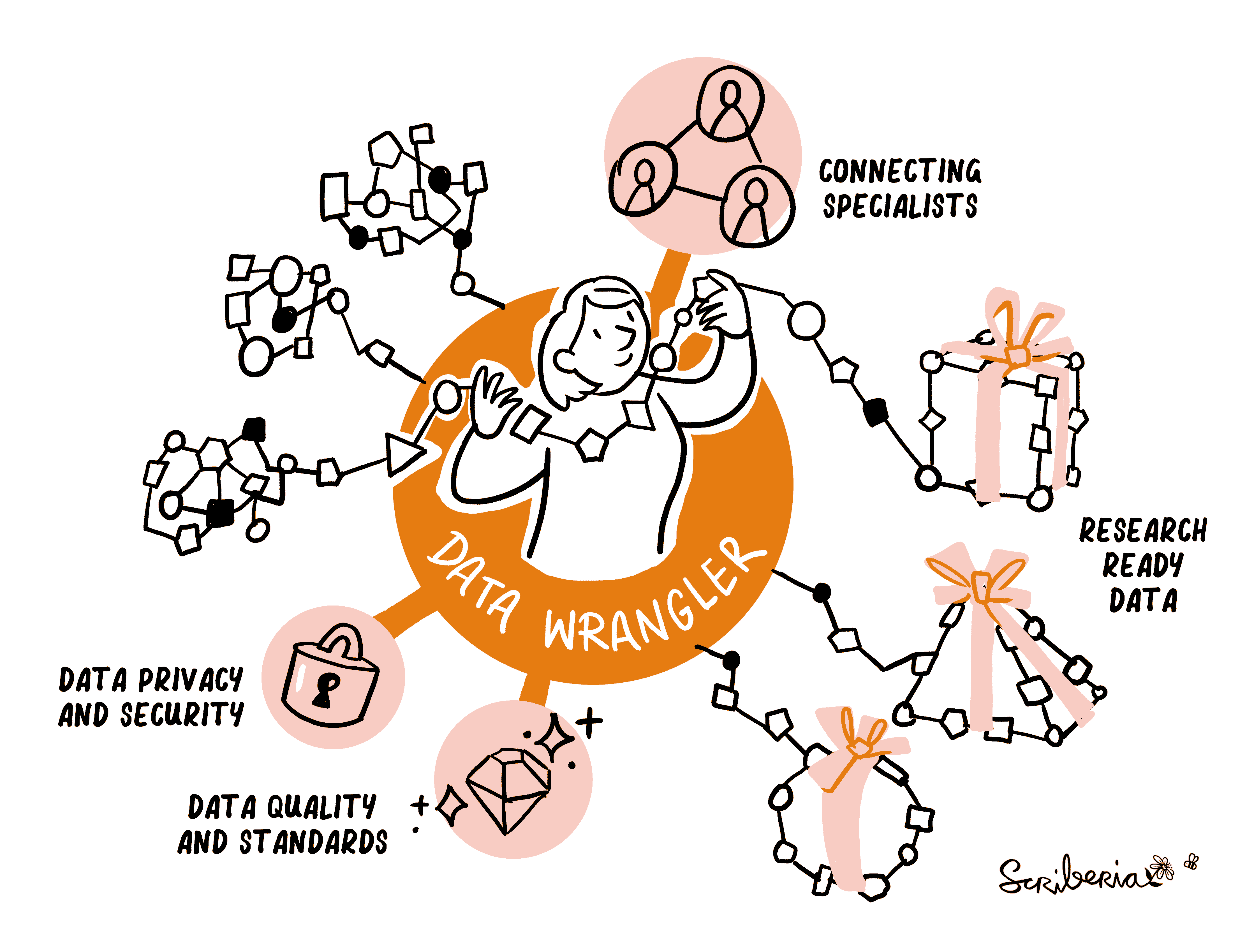
Figure 1:A Data Wrangler collaborates with multiple specialists to provide research-ready data whilst upholding data privacy and domain-specific standards. Created by Scriberia with The Turing Way community. Used under a CC-BY 4.0 licence. DOI: The Turing Way Community & Scriberia (2024).
What do Data Wranglers do?¶
In a data science project, it is commonly observed that data wrangling tasks take the majority of time Anaconda, 2020, in contrast to data analysis and modelling. Traditionally, data wrangling tasks involve cleaning, restructuring and filtering data into analysis-ready formats. However, in terms of Data Wrangler as a profession, day to day tasks and objectives can be much more diverse.
Data Wranglers work primarily in the space between data generators and data analysts, who are addressing the research question of interest. Understanding the intended use for the data in the context of the analysis and research questions, Data Wranglers can be in the position of influencing data generators in improving data collection methods. Similarly, Data Wranglers will conduct preliminary analysis on the data to ensure both completeness of data and preparation for data analysis, acting as a proxy for the data generator’s knowledge during the data analysis process. A key focus of a Data Wrangler’s role is the preparation of analysis/research-ready data Stewart et al., 2022 in which data security, data management and FAIR standards Mons et al., 2017 are all core priorities.
Examples of day-to-day tasks:¶
Data retrieval, querying, data analysis and visualizations
Data pipeline development, maintenance and improvement
Communicating with domain and technical experts
Data privacy and infrastructure setup and management
Summarising domain specific research papers
Sharing and reviewing resources and code
Maintaining communication across multiple teams
Running workshops on data wrangling and related skills
What qualifications or skills do you need to be a Data Wrangler?¶
Data Wranglers should have experience with programming (no specific language required, but there is a wider adoption of both R and Python), database querying (SQL) and data analysis.
They will have an educational background to equip them to engage with the specific research data objects relevant to the projects they will work on.
Therefore, they will have undergraduate and postgraduate degrees, or equivalent experience.
As with many data science and research infrastructure roles, further relevant training and specialisation can happen on the job.
They need good problem solving skills, with a curiosity and willingness to learn.
Lastly, good interpersonal skills are required in order to work with people with many different backgrounds, skillsets and priorities.
Challenges for Data Wranglers¶
Some key challenges of a Data Wrangler role are:
Immutable data collection methods (unable to change how data has been collected and stored)
Stringent data privacy requirements
Difficulties in accessing datasets
Lack of or missing documentation on data generation, data structure and contextual information
Insufficient resources (human, computational, economic)
Unclear scope of responsibilities within the project
In an ideal situation, some of these challenges can be mitigated if communication with Data Wranglers near the start of a project is encouraged and facilitated.
Benefits of having Data Wranglers¶
Improved communication between stakeholders: Data Wranglers will mediate the ‘language barriers’ between the different people involved in collecting the data, analysing the data and interpreting the data.
Centrally coordinated efforts: Data Wranglers can collect common questions and discussion topics of interest and provide answers and resources.
Data Wranglers will provide expertise in data collection, structuring and quality assurance. This can decrease the time it takes to go from data provider to data analysis, whilst also improving analysis quality and focus.
Data Wranglers can ensure a project keeps up to date with field specific knowledge and standards relevant to data processing and sharing, and communicate this back to the project team.
By participating and contributing to data analysis meetings and tasks, Data Wranglers can provide the best suitable datasets for the analysis, help understand and overcome challenges, and suggest further research paths.
Who employs Data Wranglers?¶
Here are some examples of places that employ Data Wranglers in the UK:
The Big Data Institute, Oxford University
Project: Novartis collaboration
EMBL’s European Bioinformatics Institute
Project: The Human Cell Atlas
NHS England
Project: NHSE Secure Data Environment
Description: NHS England Data Wranglers support a wide range of research done by health and social care organisations using the National Secure Data Environment (NSDE) to ensure the data is in an accessible format. They also help suggest and test platform improvements, produce “here’s one I made earlier” analyses, to save users time and advise on data in a technical capacity.
Please get in touch if you know of other organisations that you would like to add to this list. This list, and this Data Wrangler page in general, started off with a focus on Data Wrangler roles within an academic research context, but these roles will also exist within other contexts.
Data Wranglers: Summary¶
A Data Wrangler position is becoming recognised as a crucial part of any project that involves large amounts of complex data, specifically in a research context. They will have a diverse set of technical and interpersonal skills. A Data Wrangler will bring dedicated time and resources to increasing data quality whilst facilitating collaboration, ultimately resulting in more efficient and impactful project outcomes.
- The Turing Way Community, & Scriberia. (2024). Illustrations from The Turing Way: Shared under CC-BY 4.0 for reuse. Zenodo. 10.5281/ZENODO.3332807
- Anaconda, Inc. (2020). 2020 STATE OF DATA SCIENCE (pp. 11–12). https://know.anaconda.com/rs/387-XNW-688/images/Anaconda-SODS-Report-2020-Final.pdf
- Stewart, B., Oliver, E., & McGrath-Lone, L. (2022). What is ‘research-ready’ data? https://www.adruk.org/fileadmin/uploads/adruk/Documents/What_is_research_ready_data__A_roundtable_report_June_2022.pdf
- Mons, B., Neylon, C., Velterop, J., Dumontier, M., Bonino da Silva Santos, L. O., & Wilkinson, M. (2017). Cloudy, increasingly FAIR; Revisiting the FAIR Data guiding principles for the European Open Science Cloud. Information Services & Use, 37, 1–8. 10.3233/ISU-170824